My Research
Publications
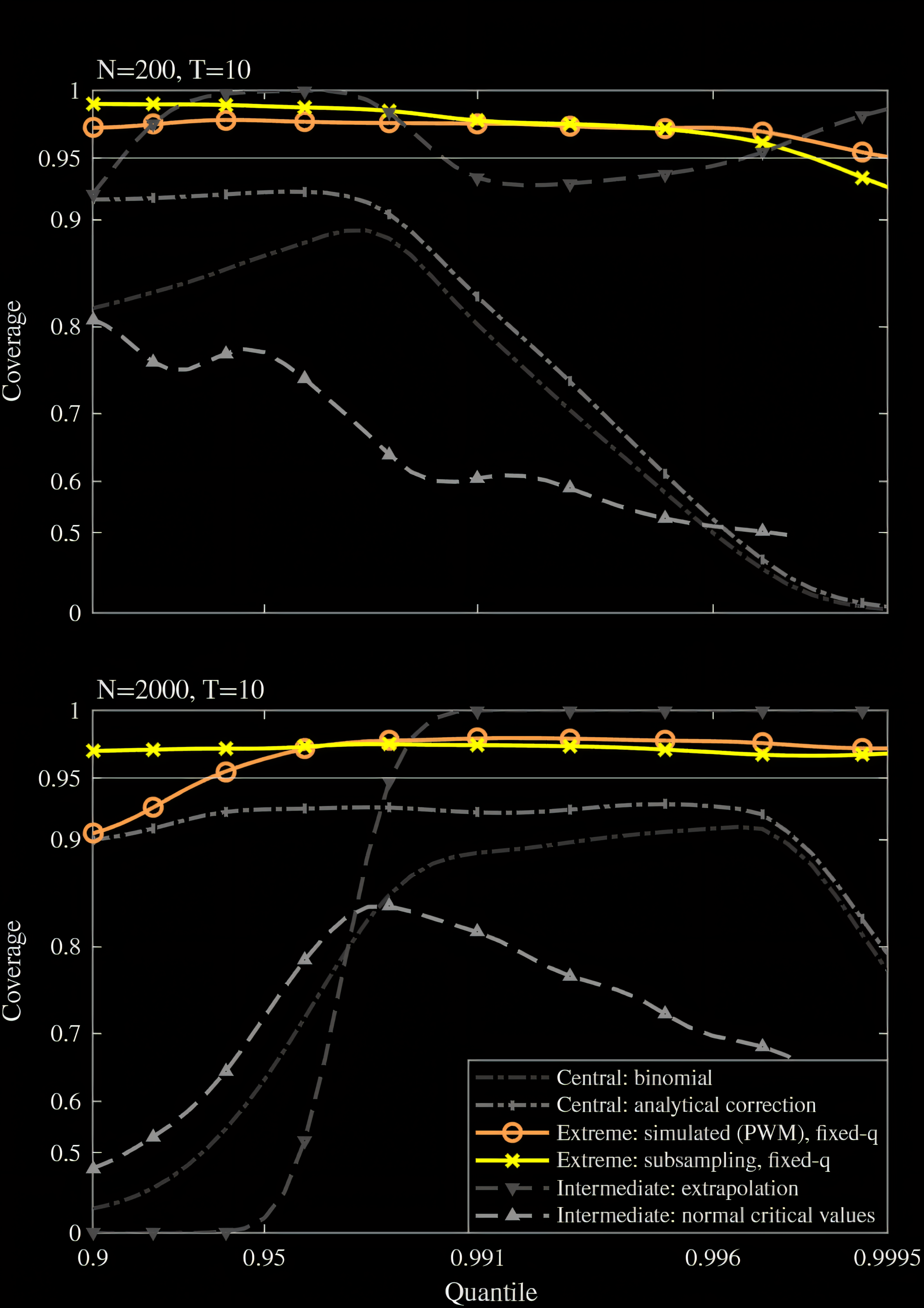
Inference on Extreme Quantiles of Unobserved Individual Heterogeneity
Econometric Theory , 2026




We develop a methodology for conducting inference on extreme quantiles of unobserved individual heterogeneity (e.g., heterogeneous coefficients, treatment effects) in panel data and meta-analysis settings. Inference is challenging in such settings: only noisy estimates of heterogeneity are available, and central limit approximations perform poorly in the tails. We derive a necessary and sufficient condition under which noisy estimates are informative about extreme quantiles, along with sufficient rate and moment conditions. Under these conditions, we establish an extreme value theorem and an intermediate order theorem for noisy estimates. These results yield simple optimization-free confidence intervals for extreme quantiles. Simulations show that our confidence intervals have favorable coverage and that the rate conditions matter for the validity of inference. We illustrate the method with an application to firm productivity differences between denser and less dense areas.
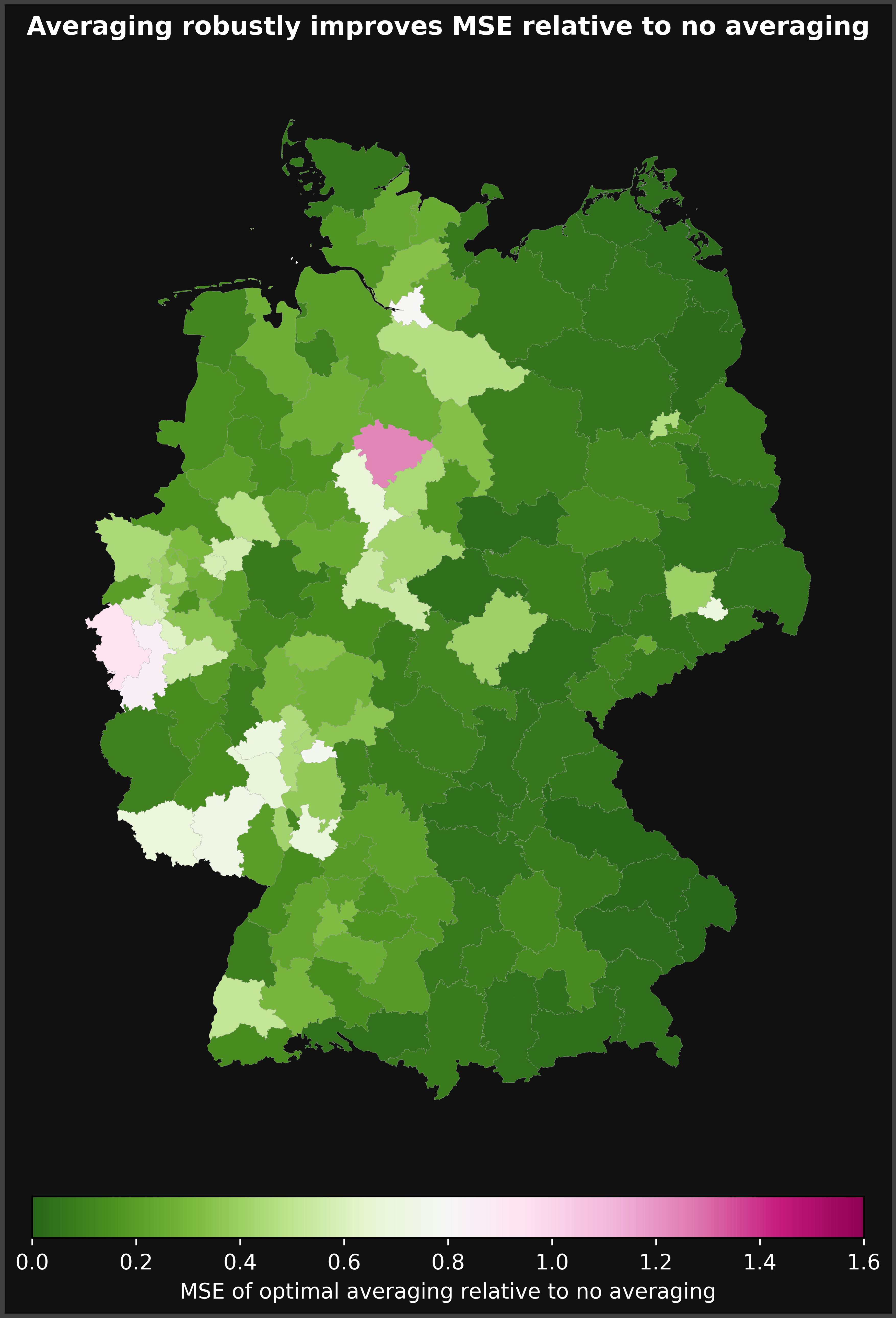
Unit Averaging for Heterogeneous Panels
Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 2025





In this work we introduce a unit averaging procedure to efficiently recover unit-specific parameters in a heterogeneous panel model. The procedure consists in estimating the parameter of a given unit using a weighted average of all the unit-specific parameter estimators in the panel. The weights of the average are determined by minimizing an MSE criterion. We analyze the properties of the minimum MSE unit averaging estimator in a local heterogeneity framework inspired by the literature on frequentist model averaging. The analysis of the estimator covers both the cases in which the cross-sectional dimension of the panel is fixed and large. In both cases, we obtain the local asymptotic distribution of the minimum MSE unit averaging estimators and of the associated weights. A GDP nowcasting application for a panel of European countries showcases the benefits of the procedure.
Working Papers
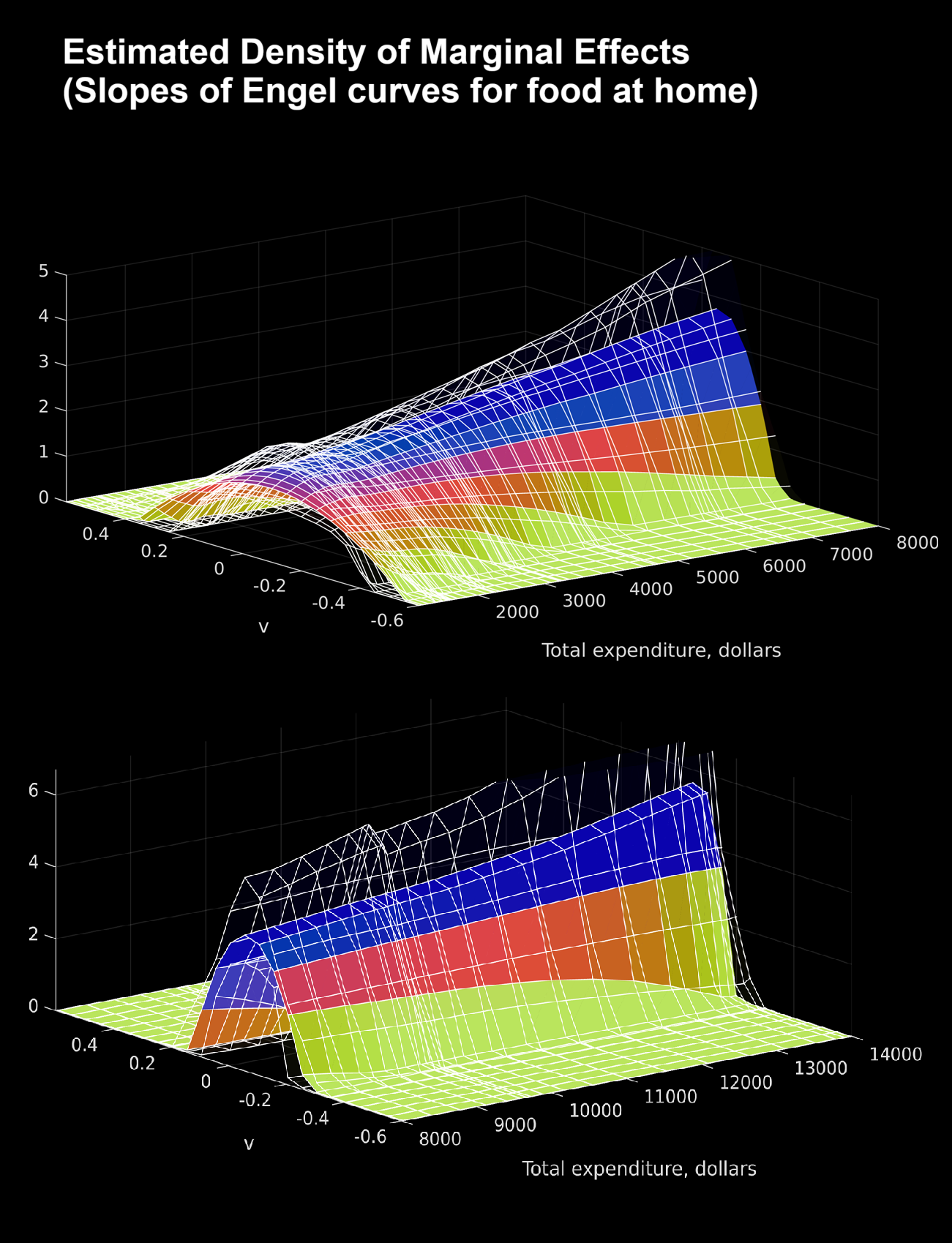
Estimating The Moments and the Distribution of Heterogeneous Marginal Effects Using Panel Data

This paper considers estimation of the moments and the distribution of heterogeneous marginal effects using panel data. We impose no restrictions on the form or dimension of time-invariant heterogeneity. In this setting, we identify the mean, variance, higher-order moments, and the distribution of marginal effects using two periods of data. We propose simple nonparametric estimators for the moments and the distribution, and study their asymptotic properties. The moment estimators are consistent and asymptotically normal. For the distribution estimator, we establish consistency by developing novel results that connect the convergence of distributions to the convergence of their moments. We illustrate the methodology with an application to Engel curves for food at home. Our analysis of variance, higher moments, and the distribution of marginal effects reveals significant heterogeneity. In particular, some households have upward-sloping sections in their Engel curves for lower values of expenditures. In contrast, the average Engel curve is downward-sloping for all expenditure values, in line with the previous literature.
Work in Progress
- Deconvolution Estimation and Inference on the Distribution of Marginal Effects
- Simple and Powerful Linear Sieves for Conditional Distributions
- Limits of Identification in Nonseparable Nonparametric Models
- Distribution Equality Tests With Noisy Observations (with Andrea Sy)
